Stop #27 - Paying for coffee in bitcoin
"Lightning Network is more convenient than credit-cards," even Morgan Stanley says so. Insight into the technology that enables instant bitcoin transactions by solving its scalability problem
"The fees for sending bitcoin transactions through Lightning Network are close to zero, so for making small payments, Lightning is a more practical tool than a debit card."
This quote is part of a study released this week by Morgan Stanley, one of the world's largest investment banks. But what is the Lightning Network? While mentioning it in the previous episodes I wrote that I would devote an entire stop of in-depth analysis and since every promise is a debt, here I am to keep it1.
Lightning Network: A Solution to Scalability
The inefficiency of the blockchain
The issue of scalability has always been one of the thorniest for Bitcoin. As written in stop #23 the security and the wide decentralization of the network involve an inevitable trade-off, that of a slow and inefficient blockchain in terms of the amount of transactions supported (on average only 280 thousand per day2).
In order to avoid a centralization of the network by expanding the capacity of Bitcoin's basic blockchain - also known as Layer 1 - the community arrived at a solution that allows for instant and potentially unlimited payments in bitcoin but without touching the blockchain. In 2015, Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja published a paper titled The Bitcoin Lightning Network: scalable Off-Chain Instant Payments and three years later, the Lightning Network - also known as Layer 2 and abbreviated to LN - began its operations.
A layer on top of a layer
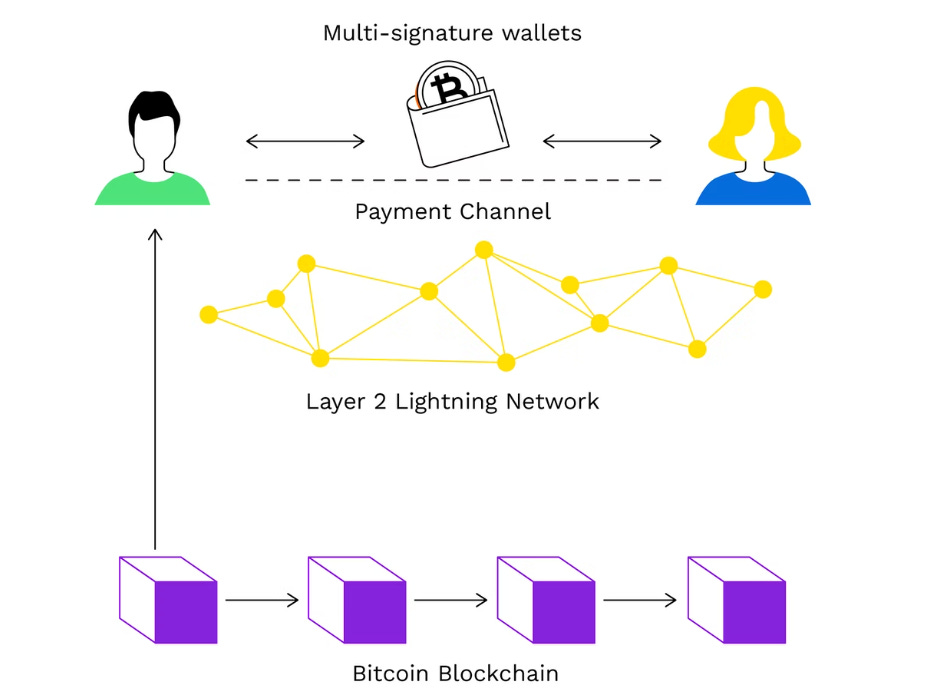
Above Bitcoin's Layer 1, consisting of roughly 50 thousand nodes distributed around the world, there is now a Layer 2, with about 17 thousand nodes, which allows its members to exchange money without registering transactions on the blockchain thus saving time and fees.
Let's start with an analogy: if we were obliged to always pay in cash by taking it out of the safe every time, every transaction would be long and cumbersome. Let's suppose we take some cash from the safe - for example $100 - and put it in a wallet dedicated only to transactions with another person, Alice. Alice decides to do the same thing and puts € 100 from her safe into the wallet.
The wallet now contains $200 in cash, of which $100 is mine and $100 is Alice's. Every time a payment is made from me to Alice or vice versa, the internal balance is updated. So, if I pay $50 to Alice, her balance will be $150 and mine $50, but the overall balance will still be $200. When we finally decide that we don't need the wallet any more, we can withdraw the updated balances - $50 for me and $150 for Alice - and put the respective cash back in our safes.
In extremely simplified terms, this is the basic operation of the Lightning Network.
Payment channels and multi-sig wallets
In the Bitcoin context, the safe is the blockchain, Alice and I are the nodes in the network, and the wallet is a payment channel.
When two nodes want to make fast, commission-free transactions with each other what happens is the following:
On the blockchain, node A signs together with node B a multisig transaction 2 of 23 thereby blocking a predefined amount, for example 0.3 bitcoin.
The transaction, like all on-chain4 transactions, is approved and recorded in a block. This opens a payment channel between node A and node B with a total balance of 0.3 bitcoins.
The two nodes can start exchanging an unlimited number of payments with the amount that has been deposited in the channel. Each transaction updates the balance of the two nodes but without recording any information on the blockchain, therefore not having to wait for any confirmation it’s done instantly.
Let’s suppose that after 310 transactions have taken place, the two nodes determine that the channel is no longer needed. The balance is 0.05 bitcoin for node A and 0.25 bitcoin for node B. The two nodes sign a 2-of-2 multisig transaction on the bitcoin blockchain assigning 0.05 bitcoin to node A and 0.25 bitcoin to node B.
The payment channel is closed and the two parties have exchanged more than 300 payments by writing only two transactions on the blockchain: the opening (settlement) and closing (commitment) of the channel.
Payments routing
The most attentive readers may have a doubt: to use LN, do I have to open a channel with all the people with whom I intend to exchange payments? The answer, of course, is no.
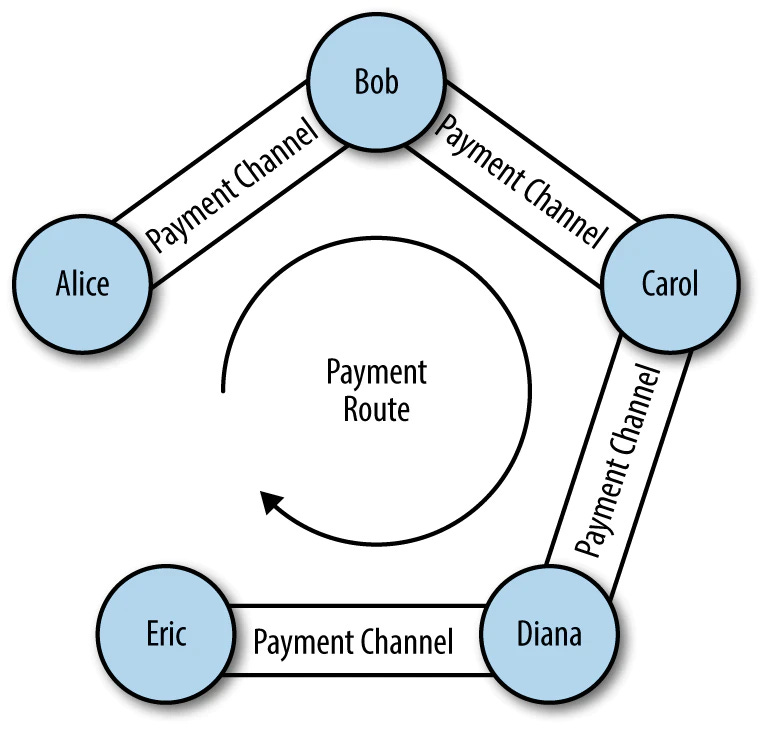
As anticipated, the Lightning Network is also a network. This means that nodes are interconnected and, in addition to exchanging payments with the nodes with which they have open channels, they can also transport payments from other nodes: a process known as routing.
Node A can send a payment to node D as long as there is a path for the transaction to reach its destination. So if node A has a channel to node B, node B has a channel to node C, and node C has a channel to node D, then node A can pay node D (and vice versa). The process by which a node looks for a way to bring a payment to its destination is called pathfinding.
The best way to take advantage of Lightning Network technology is to have a well-connected node - therefore with numerous payment channels to other nodes - but this is not a fundamental requirement. It is also possible to receive and send Lightning transactions with wallets that allow you to use their nodes: Blue, Muun & Phoenix are among the best known.
Consequences and diffusion of the Lightning Network
Only 4 years after its birth, the LN is proving to be a technology capable of revolutionizing the world market of small and medium payments: eliminating the intermediaries involved in card transactions - banks and circuits - entails big savings in terms of time and commissions.
Companies like Strike, then, allow to send digital payments in dollars exploiting the Lightning Network protocol, making instant transactions possible and eliminating the risk of volatility for those customers who do not know or do not want to hold bitcoin. For similar purposes, the development of those who do research on Bitcoin is also fervent: protocols like RGB (one of whose minds is the Italian Giacomo Zucco) and Taro - which are not yet implemented but in an advanced stage of development - aim to use LN to allow the transfer of assets other than bitcoin.
In El Salvador, where the cryptocurrency introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto was made legal tender last year, the Lightning Network is used on a daily basis and some have documented small transactions such as paying for a coffee in places like, say, a very common McDonald's.
The state of the art
The growth of Layer 2 was recently captured by Arcane Research and Open Node's The State of Lightning report, which reported how the volume of dollar payments made off-chain grew 410% over last year.
Specifically, as of February 2022, Layer 2 hosted just over 500,000 transactions for a total of $20 million transacted: an average of $40 per payment. Yes, because LN is not designed for large transactions.
The network's security, while much higher than the traditional payment networks we all use, is inferior when compared to the inviolability and immutability that Bitcoin's blockchain guarantees, which will be increasingly suitable for sending and receiving significant sums.
It's perhaps convenient to think of Bitcoin's two tiers as one's bank account and wallet. One for larger payments, the other for smaller, more immediate ones.
Translated by Guglielmo
HOW TO BUY BITCOIN?
Personally, what I consider as the best service is Relai. To buy bitcoin saving 0.5% in commissions you can use the code "FEDERICO".
This is an application developed by a Swiss company that applies a KYC light policy: unlike the big exchanges it doesn't require registration or personal data, all you need to buy bitcoin is your IBAN. It is optimal for setting up savings plans.
One of the best features is the non-custodial service. Euros transferred to Relai are automatically converted into bitcoin and transferred to a wallet over which only the user has control. Big exchanges, on the contrary, do not provide private keys to customers. Plus, Relai does not sell hundreds of useless cryptocurrencies, only bitcoin.
NOTE - This is NOT an advertising message. Relai is a service that I personally use and I consider one of the best on the market in terms of reliability, security and ease of use. I often recommend it to friends and family. What do I earn? What the referral code makes me earn. In this case if you buy with the code "FEDERICO" you save 0.5% on commissions and I receive (in bitcoin) 0.5% of the amount you have decided to invest.
Disclaimer: since Bitcoin Train is not a newsletter dedicated to a technical reader, I will voluntarily limit myself to explain the functioning of Lightning Network in brief, computer scientists will excuse me. For any doubt or desire to deepen write me and I will be happy to answer. If I receive many requests I will consider a new stop that goes into more detail about the technology.
Bitcoin's blockchain hosts roughly 280 thousand transactions per day, while large centralized (and as such more efficient) networks like Mastercard and Visa process 366 million and 597 million transactions, respectively.
As explained in stop #7, the multisig (short for multi-signature) feature allows a wallet to be managed with multiple keys. If the board of directors of a company, for example, wanted to control their bitcoins in a distributed fashion, they could use a wallet with 5 keys (a number that is entirely illustrative) and establish that transactions can only be made if they are signed by the majority, for example 3 out of 5. A 2-of-2 multisig wallet would only allow funds to be moved with the signature of both parties.
Payments made on Bitcoin's blockchain are referred to as on-chain, those on Lightning Network are referred to as off-chain.